Archives
- 2026-02
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-04
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-07
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2019-06
- 2019-05
- 2019-04
- 2018-11
- 2018-10
- 2018-07
-
Findings Between July and March we enrolled
2019-04-29
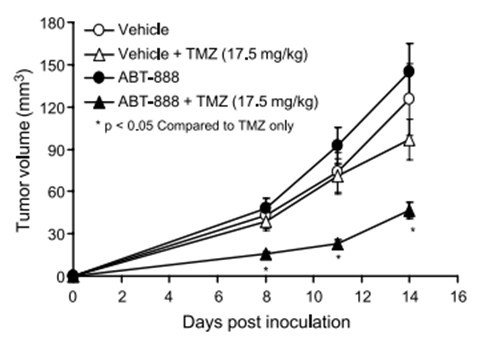
Findings Between July, 2013, and March, 2015, we enrolled 324 pregnant women (162 to each study group); 18 women were lost to follow up before delivery. Measurements of biomarkers made more than 60 days before randomisation (17 participants) or more than 300 days after randomisation (26 participants
-
Outbreaks of carbapenem resistant A baumannii carrying blaOX
2019-04-29
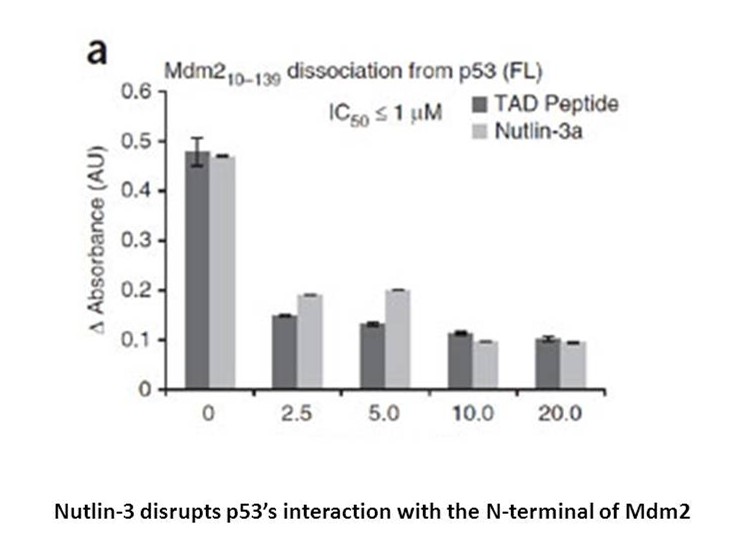
Outbreaks of carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii carrying blaOXA-23-like were discovered in different countries, and the range of blaOXA-23-like has been reported from 31% to 100% worldwide. In our study, the vast majority of isolates (70%) were positive for blaOXA-23-like. Moreover, we found that 20%
-
The ideal treatment end point
2019-04-28
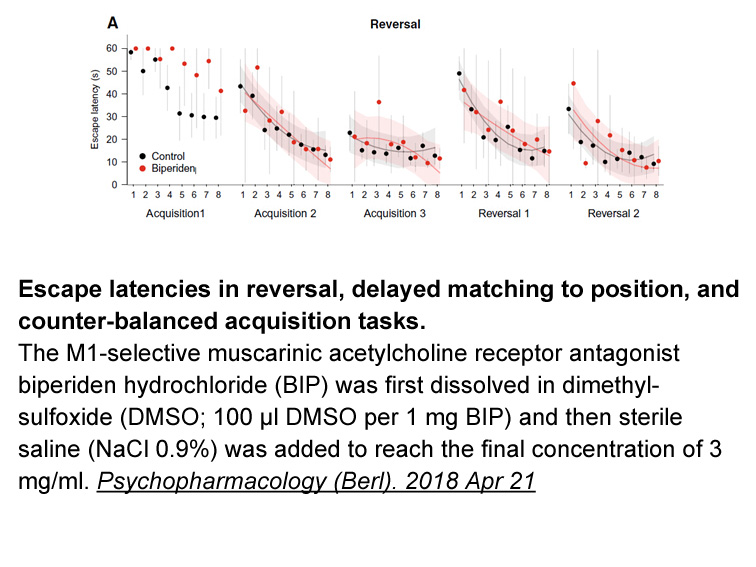
The ideal treatment end-point is sustained HBsAg loss with or without anti-HBs seroconversion in HBeAg-positive and HBeAg-negative patients. Actually, the duration of ETV treatment for HBeAg positive CHB may be up to 240 weeks. A duration of consolidation therapy after HBeAg seroconversion is indica
-
Scott Mainwaring enfatiza que a ascens o do comunismo
2019-04-28
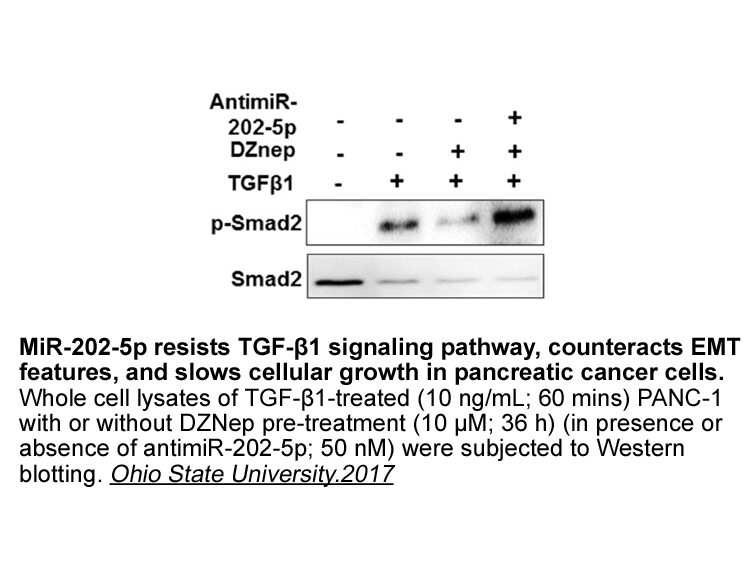
Scott Mainwaring enfatiza que ABT888 ascensão do comunismo e do movimento sindical mobilizou a adesão de boa parte dos católicos ao movimento integralista (de inspiração conservadora). Além das campanhas de “demonização” desta orientação política e de seus membros, a Igreja criou no início da década
-
Fischer and colleagues also raise concerns about the fact th
2019-04-28
Fischer and colleagues also raise concerns about the fact that MHSP “only offers testing to men”. As previously stated, MHSP is a public health programme based on the principles outlined in WHO\'s interim guidelines. The focus of that guidance is preventing sexual transmission of Ebola virus by men
-
After permanent pacemaker implantation the lead electrocardi
2019-04-28
After permanent pacemaker implantation, the 12-lead electrocardiogram revealed that the pacing spike appeared at the same time as the P wave and narrow QRS complexes with AV conduction (Fig. 4). This finding demonstrated effective enforcement of the left atrial pacing. The patient had no postoperati
-
We are aware that physician surveys
2019-04-28
We are aware that physician surveys have been previously used to assess; bisphosphonate use for bone pain [14], bisphosphonate use in metastatic breast cancer patients [15] and radiotherapy use for painful bone metastases [16] but are not aware of physician surveys being used to help design trials o
-
br Discussion Metastatic RCC is a fatal disease with surviva
2019-04-28

Discussion Metastatic RCC is a fatal disease with survival often measured in months, rather than years. Surgery alone is the standard of care for patients who present with isolated renal disease at the time of diagnosis. However, approximately 1/3 of these patients will go on to develop clinicall
-
stavudine La Constituci n espa ola
2019-04-28
La Constitución española de 1812 dispone bajo el nombre de América septentrional un territorio que desde California, Nuevo México y Texas hasta la Capitanía de Guatemala conforma una inmensa, compleja y rica estructura administrativa. Guatemala se separa poco antes de la jura de la Constitución de 1
-
buy dihydroergotamine mesylate br Chronic obstructive pulmon
2019-04-28
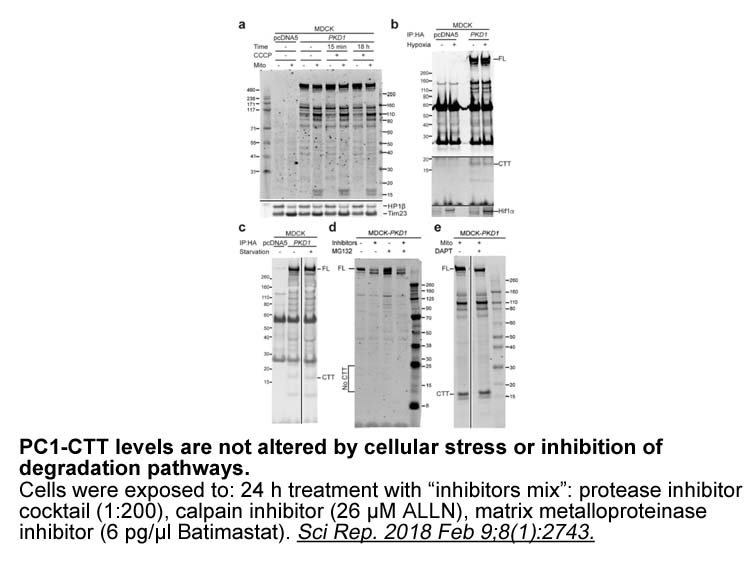
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) remains a major public health problem. The was first published by the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) in 2001. A major revision was undertaken in 2011 and an update to it was published in February this year. The Chinese So
-
br Although much attention centres on
2019-04-28
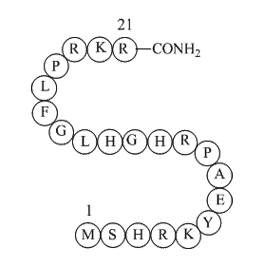
Although much attention centres on Afghanistan\'s political and security transitions, malnutrition is a foremost concern. Because an absence of adequate nutrition has crucial long-term effects on individuals and on social and economic development, nutrition rates in Afghanistan deserve attention a
-
Nevertheless we believe that the
2019-04-28
Nevertheless, we believe that the main findings of our study are robust. We noted a progressive increase in the prevalence of rheumatic metabolic enzymes disease with advancing age of children, modelling different prevalence patterns across age groups separately for each study, and pooling estimates
-
Ya en el siglo xx
2019-04-28
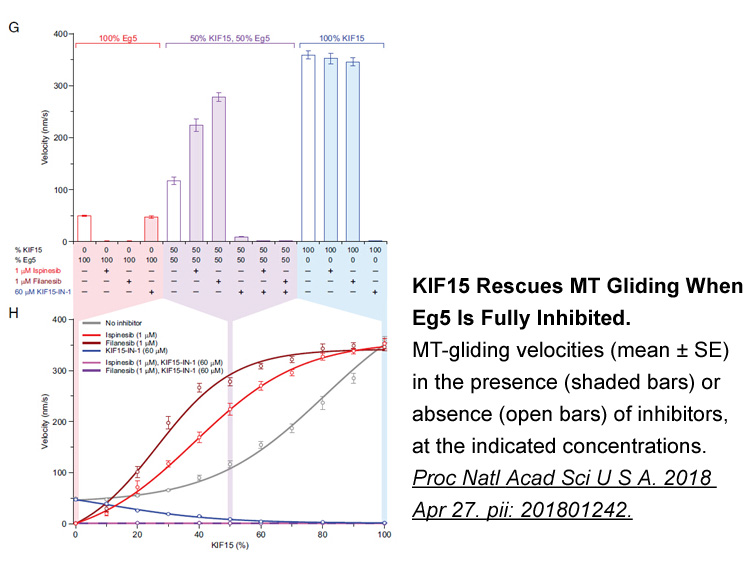
Ya en el siglo xx, la Historia verdadera (y las crónicas de Indias en general) ha sido recuperada como origen de la literatura latinoamericana contemporánea, en especial por escritores vinculados orexin la literatura del boom: Alejo Carpentier, Gabriel García Márquez, Carlos Fuentes. De hecho, Fuent
-
glycogen synthase kinase br Hacia un monote smo ta no Debido
2019-04-28
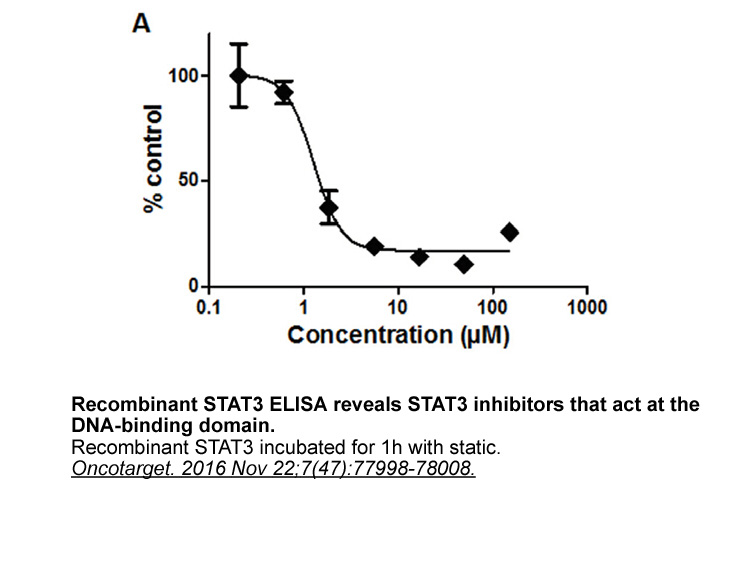
Hacia un monoteísmo taíno Debido al hecho de que la irreductible diversidad de los cemíes parece demasiado peligrosa para ser comparada con la noción antigua de divinidad, la Relación trata de proponer, aunque de manera discreta, otra forma de interpretación: es decir, la búsqueda de las huellas
-
Asimismo y con distinto nfasis entre s
2019-04-28
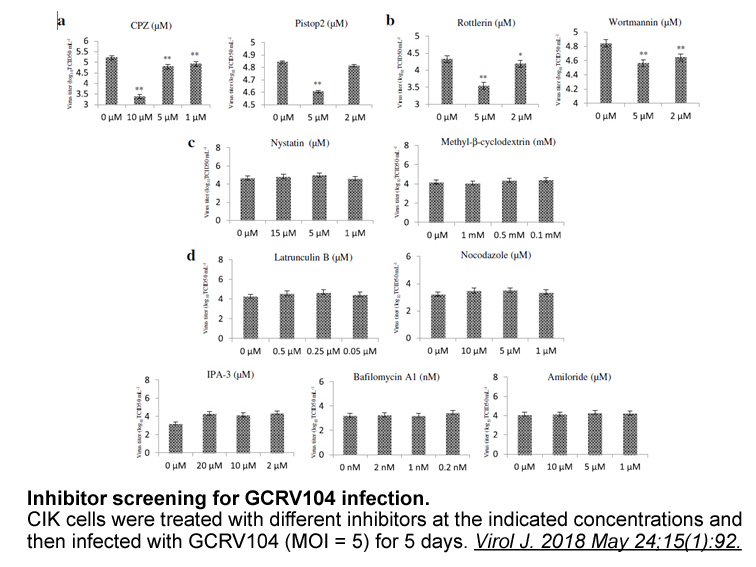
Asimismo y con distinto énfasis entre sí, estas crónicas presentan la dimensión de la escritura de la historia como reparación, como sutura del trauma, y también como espacio textual único para la supervivencia de memorias en constante proceso de desaparición. Esto les confiere cierto ubicuo tono de
15946 records 1031/1064 page Previous Next First page 上5页 10311032103310341035 下5页 Last page